-
[백준] 1726번 로봇Algorithm Study/Python 2021. 7. 28. 23:36
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1726
1726번: 로봇
많은 공장에서 로봇이 이용되고 있다. 우리 월드 공장의 로봇은 바라보는 방향으로 궤도를 따라 움직이며, 움직이는 방향은 동, 서, 남, 북 가운데 하나이다. 로봇의 이동을 제어하는 명령어는
www.acmicpc.net
문제
많은 공장에서 로봇이 이용되고 있다. 우리 월드 공장의 로봇은 바라보는 방향으로 궤도를 따라 움직이며, 움직이는 방향은 동, 서, 남, 북 가운데 하나이다. 로봇의 이동을 제어하는 명령어는 다음과 같이 두 가지이다.
- 명령 1. Go k: k는 1, 2 또는 3일 수 있다. 현재 향하고 있는 방향으로 k칸 만큼 움직인다.
- 명령 2. Turn dir: dir은 left 또는 right 이며, 각각 왼쪽 또는 오른쪽으로 90° 회전한다.
공장 내 궤도가 설치되어 있는 상태가 아래와 같이 0과 1로 이루어진 직사각형 모양으로 로봇에게 입력된다. 0은 궤도가 깔려 있어 로봇이 갈 수 있는 지점이고, 1은 궤도가 없어 로봇이 갈 수 없는 지점이다. 로봇이 (4, 2) 지점에서 남쪽을 향하고 있을 때, 이 로봇을 (2, 4) 지점에서 동쪽으로 향하도록 이동시키는 것은 아래와 같이 9번의 명령으로 가능하다.
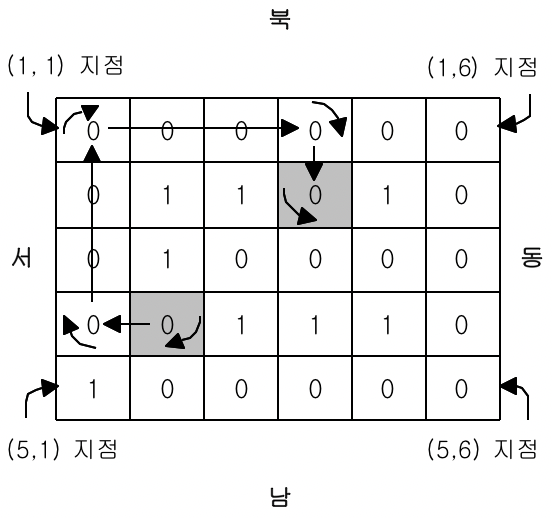
로봇의 현재 위치와 바라보는 방향이 주어졌을 때, 로봇을 원하는 위치로 이동시키고, 원하는 방향으로 바라보도록 하는데 최소 몇 번의 명령이 필요한지 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫째 줄에 공장 내 궤도 설치 상태를 나타내는 직사각형의 세로 길이 M과 가로 길이 N이 빈칸을 사이에 두고 주어진다. 이때 M과 N은 둘 다 100이하의 자연수이다. 이어 M줄에 걸쳐 한 줄에 N개씩 각 지점의 궤도 설치 상태를 나타내는 숫자 0 또는 1이 빈칸을 사이에 두고 주어진다. 다음 줄에는 로봇의 출발 지점의 위치 (행과 열의 번호)와 바라보는 방향이 빈칸을 사이에 두고 주어진다. 마지막 줄에는 로봇의 도착 지점의 위치 (행과 열의 번호)와 바라보는 방향이 빈칸을 사이에 두고 주어진다. 방향은 동쪽이 1, 서쪽이 2, 남쪽이 3, 북쪽이 4로 주어진다. 출발지점에서 도착지점까지는 항상 이동이 가능하다.
출력
첫째 줄에 로봇을 도착 지점에 원하는 방향으로 이동시키는데 필요한 최소 명령 횟수를 출력한다.

풀이
BFS를 이용하여 도착하는데까지 걸리는 시간을 나타내면 될 것이라고 생각했다.
이동하는 방법은 1 ~ 3칸 전진 또는 좌회전 우회전만 있기 때문에 기존의 4방향으로 퍼지는 방식이 아니라
1~3칸 전진, 좌회전, 우회전, 후진 4가지로 나누어서 계산하였다.Time Limit Exceed code
더보기import sys from collections import deque ROW, COL = map(int , sys.stdin.readline().split()) board = [list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())) for _ in range(ROW)] visited = [[False for _ in range(COL)] for _ in range(ROW)] dq = deque() flag = False # 방향을 1칸만 이동하면 좌회전 우회전을 할 수 있음 기존의 1 2 3 4로 구현하면 회전이 복잡해진다. direction = [[-1, 0], [0, -1], [1, 0], [0, 1]] start_y, start_x, start_dir = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split()) end_y, end_x, end_dir = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split()) # 좌우로 쉽게 돌리기 위해서 좌표에 대한 전처리 if start_dir == 1: start_dir = 3 elif start_dir == 2: start_dir = 1 elif start_dir == 3: start_dir = 2 elif start_dir == 4: start_dir = 0 if end_dir == 1: end_dir = 3 elif end_dir == 2: end_dir = 1 elif end_dir == 3: end_dir = 2 elif end_dir == 4: end_dir = 0 dq.append((start_y-1, start_x-1, start_dir, 0)) while dq: dq_size = len(dq) while dq_size: now_y, now_x, now_dir, count = dq.popleft() dq_size -= 1 if now_y == end_y-1 and now_x == end_x-1: if now_dir == end_dir: print(count) elif (now_dir + 1 + 4) % 4 == end_dir or (now_dir - 1 + 4) % 4 == end_dir: print(count+1) else: print(count+2) flag = True break # 1칸 ~ 3칸 전진 for i in range(1, 4): next_y, next_x = now_y + direction[now_dir][0]*i, now_x + direction[now_dir][1]*i if 0 <= next_y < ROW and 0 <= next_x < COL: if board[next_y][next_x] == 0 and not visited[next_y][next_x]: dq.append([next_y, next_x, now_dir, count + 1]) visited[next_y][next_x] = True elif board[next_y][next_x] == 1: break #좌회전 dq.append([now_y, now_x, (now_dir + 1 + 4) % 4, count + 1]) #우회전 dq.append([now_y, now_x, (now_dir - 1 + 4) % 4, count + 1]) #후진 dq.append([now_y, now_x, (now_dir + 2 + 4) % 4, count + 2]) if flag: breakvisited 배열로 방문을 체크하였는데 회전하는 경우에는 방문에 대한 체크가 이루어지지 않았기 때문에
시간초과가 발생하였다.#3차원 dist배열 활용 각 방향의 상태 저장 dist = [[[-1 for _ in range(4)] for _ in range(COL)] for _ in range(ROW)]1바퀴 회전을 해서 같은 방향으로 다시 돌아오는 경우를 제거하기 위해서 방문을 나타내는 배열을 3차원으로 만들어서 사용했다. Y, X, DIR 3가지 인자를 표기하기 위해서다.
# 방향을 1칸만 이동하면 좌회전 우회전을 할 수 있음 기존의 1 2 3 4로 구현하면 회전이 복잡해진다. direction = [[-1, 0], [0, -1], [1, 0], [0, 1]] # 좌우로 쉽게 돌리기 위해서 좌표에 대한 전처리 if start_dir == 1: start_dir = 3 elif start_dir == 2: start_dir = 1 elif start_dir == 3: start_dir = 2 elif start_dir == 4: start_dir = 0 if end_dir == 1: end_dir = 3 elif end_dir == 2: end_dir = 1 elif end_dir == 3: end_dir = 2 elif end_dir == 4: end_dir = 0또 기존의 문제에서 동서남북의 순서가 복잡하게 되어 있어서 임의로 수정한 뒤
입력으로 들어오는 방향을 수정한 방향에 따라서 변경했다.
이렇게 변경하면 현재 Index에서 +1하는 것으로 좌회전, -1하는 것으로 우회전을 구현할 수 있다.# 1칸 ~ 3칸 전진 for i in range(1, 4): next_y, next_x = now_y + direction[now_dir][0]*i, now_x + direction[now_dir][1]*i if 0 <= next_y < ROW and 0 <= next_x < COL: if board[next_y][next_x] == 0 and dist[next_y][next_x][now_dir] == -1: dq.append([next_y, next_x, now_dir]) dist[next_y][next_x][now_dir] = dist[now_y][now_x][now_dir] + 1 elif board[next_y][next_x] == 1: break1 ~ 3칸 전진하기 위한 조건은 방문한 적이 없고 앞에 벽이 없으면 된다.
앞에 칸에서 벽이 발견된 경우 벽을 뛰어넘을 수 없기 때문에 break했다.#좌회전 if dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir + 1 + 4) % 4] == -1: dq.append([now_y, now_x, (now_dir + 1 + 4) % 4]) dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir + 1 + 4) % 4] = dist[now_y][now_x][now_dir] + 1 #우회전 if dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir - 1 + 4) % 4] == -1: dq.append([now_y, now_x, (now_dir - 1 + 4) % 4]) dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir - 1 + 4) % 4] = dist[now_y][now_x][now_dir] + 1 #후진 if dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir + 2 + 4) % 4] == -1: dq.append([now_y, now_x, (now_dir + 2 + 4) % 4]) dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir + 2 + 4) % 4] = dist[now_y][now_x][now_dir] + 2회전의 경우 우회전은 좌회전 3번으로 나타나기 때문에 특별한 처리를 하지 않기 위해서
좌회전, 우회전, 후진으로 나눠서 1회, 1회, 2회 이동으로 dq에 넣는 것으로 한번에 3가지 갈래로 퍼져나가는 식으로 구현하였다.전체 코드
import sys from collections import deque ROW, COL = map(int , sys.stdin.readline().split()) board = [list(map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split())) for _ in range(ROW)] #3차원 dist배열 활용 각 방향의 상태 저장 dist = [[[-1 for _ in range(4)] for _ in range(COL)] for _ in range(ROW)] dq = deque() flag = False # 방향을 1칸만 이동하면 좌회전 우회전을 할 수 있음 기존의 1 2 3 4로 구현하면 회전이 복잡해진다. direction = [[-1, 0], [0, -1], [1, 0], [0, 1]] start_y, start_x, start_dir = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split()) end_y, end_x, end_dir = map(int, sys.stdin.readline().split()) # 좌우로 쉽게 돌리기 위해서 좌표에 대한 전처리 if start_dir == 1: start_dir = 3 elif start_dir == 2: start_dir = 1 elif start_dir == 3: start_dir = 2 elif start_dir == 4: start_dir = 0 if end_dir == 1: end_dir = 3 elif end_dir == 2: end_dir = 1 elif end_dir == 3: end_dir = 2 elif end_dir == 4: end_dir = 0 dq.append((start_y-1, start_x-1, start_dir)) dist[start_y-1][start_x-1][start_dir] = 0 while dq: dq_size = len(dq) while dq_size: now_y, now_x, now_dir = dq.popleft() dq_size -= 1 if now_y == end_y-1 and now_x == end_x-1 and now_dir == end_dir: print(dist[now_y][now_x][now_dir]) flag = True break # 1칸 ~ 3칸 전진 for i in range(1, 4): next_y, next_x = now_y + direction[now_dir][0]*i, now_x + direction[now_dir][1]*i if 0 <= next_y < ROW and 0 <= next_x < COL: if board[next_y][next_x] == 0 and dist[next_y][next_x][now_dir] == -1: dq.append([next_y, next_x, now_dir]) dist[next_y][next_x][now_dir] = dist[now_y][now_x][now_dir] + 1 elif board[next_y][next_x] == 1: break #좌회전 if dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir + 1 + 4) % 4] == -1: dq.append([now_y, now_x, (now_dir + 1 + 4) % 4]) dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir + 1 + 4) % 4] = dist[now_y][now_x][now_dir] + 1 #우회전 if dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir - 1 + 4) % 4] == -1: dq.append([now_y, now_x, (now_dir - 1 + 4) % 4]) dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir - 1 + 4) % 4] = dist[now_y][now_x][now_dir] + 1 #후진 if dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir + 2 + 4) % 4] == -1: dq.append([now_y, now_x, (now_dir + 2 + 4) % 4]) dist[now_y][now_x][(now_dir + 2 + 4) % 4] = dist[now_y][now_x][now_dir] + 2 if flag: break분기를 깔끔하게 나누지 못하고 하나하나 구분했는 점이 코드가 깔끔하지는 못한 것 같다.
이정도의 로직까지는 C++로 구현할 수 있도록 연습해야겠다.'Algorithm Study > Python' 카테고리의 다른 글
[백준] 14497번 주난의 난 (0) 2021.08.10 [백준] 14567번 선수과목 (2) 2021.08.10 [백준] 1715번 카드 정렬하기 (0) 2021.07.27 [백준] 1541번 잃어버린 괄호 (0) 2021.07.27 [백준] 1476번 날짜 계산 (0) 2021.07.27